3.3.1. Columns
Columns are the small unity of a table and they define how data must be stored through their data types and additional attributes as shown in the image below.
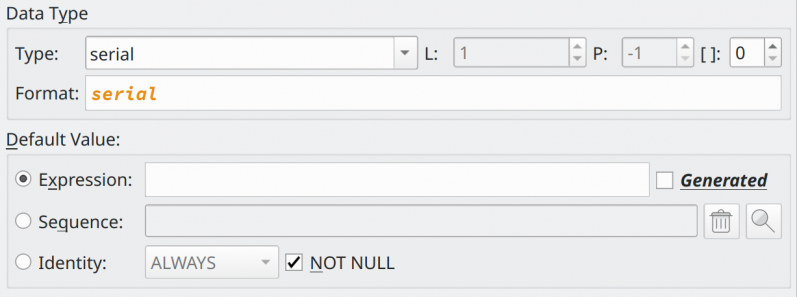
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Data Type |
This attribute handles the data type assigned to the column. |
Default Value |
This field defines the default value for the column in case none is specified in an INSERT command. If the user wants to set up a simple expression, use the attribute Expression. The Generated option indicates that the column's default value is generated from other columns' values. For example, say we have a column called height_in that represents the height in inches and another generated column called height_cm which represents the height in centimeters. The default value for height_cm can be easily computed from height_in by performing a simple conversion like height_cm / 2.54.The attribute Sequence is used to configure a default value for serial data types based upon a sequence object. Once selected, the sequence this object will be converted into an expression like: nextval('seq'::regclass). The Identity attribute is used to configure an identity column (introduced in PostgreSQL 10). The possible values of this field are ALWAYS and BY DEFAULT. In newer versions, it's possible to tweak the sequence parameters associated with the identity column. |
NOT NULL |
Creates a NOT NULL constraint in the column. |
Generated columns
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/ddl-generated-columns.html
Apr 25, 2025 at 08:47