3.17. Extensions
Extensions are modules commonly used to install additional features on a database server. Despite the extensive list of built-in extensions, PostgreSQL provides some ways for the user to write custom extensions, although this topic will not be covered in this documentation. Basically, extensions are a set of other objects, like functions, types, operators, and many others. When the user needs to install a certain extension, all the objects owned by it are installed as part of the database.
In pgModeler, an extension object is used just to tell the server that the named extension must be installed at the specified schema. To work correctly, the extension modules or libraries must exist on the database server. The extension attributes are detailed as follows.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Schema |
Specifies the schema where the objects installed by the extension will be placed by default, though extension child types can have their own schemas specified, see Types below. |
Version |
The current version of the extension to be installed. |
Old Version |
This attribute must be specified when, and only when, you are attempting to install an extension that replaces an "old style" module that is just a collection of objects not packaged into an extension. |
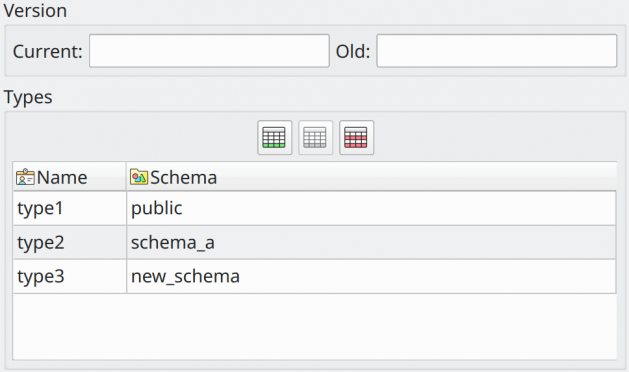
Types |
A list of types that the extension installs. Once the extension is created, the child types will be available in the data type configuration widget. If the extension is removed, the types will also be removed. The column Schema in this field specifies the schema under which the data type will be. If the schema doesn't exist in the database model, pgModeler will automatically create it as a protected object. |
Extension DDL
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/sql-createextension.html
PostgreSQL built-in extensions
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/contrib.html
Creating extensions
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/extend-extensions.html